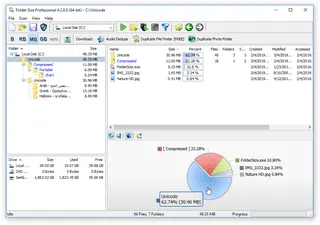
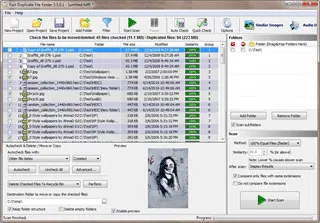
Folder Size
Folder Size explorer style freebie will list all file and folder sizes on a computer, network/NAS or external drive. This tool is tested and does not contain any malware or bundles. Here is what it can do:
- Display all folder sizes in Windows.
- List largest files and folder.
- Print all files and folders lists to printer or PDF, XML and CSV files.
- Visualize disk space distribution using beautiful Pie and Bar charts.
- List oldest/newest files and folders.
- List longest folder and file paths.
More about Folder Size explorer
Free Duplicate File Finder
Fast Duplicate File Finder will list all duplicate and similar file on a computer, network/NAS or external drive. This tool is tested and does not contain any malware or bundles. Here is what it can do:
- Find duplicate files or find similar files in user specified folders, hard drives, computers or entire networks.
- Fast binary comparison algorithm - will never report false positives.
- Internal preview supporting images, videos, music, text and binary files.
- Older or smaller files can be automatically marked for deletion.
- Clone files can be moved to Recycle Bin, custom folder or deleted permanently.
- Support for all kinds of removable media - usb/external drives.
More about Duplicate File Finder
What is Download Time?
Download time is the time needed to transfer a file from the Internet to a local machine or device. This time is determined by the connection speed and the size of the file. You calculated the download time by dividing the download size by your connections speed. Of course that result is in ideal conditions which is not always the case. Below you will find what affects download time and speed.
- How long should it take to download 1gb?
- How long does 100gb take to download?
- How long does a 10 GB download take?
- Is 16 Mbps fast?
Find the answers below.
How to Calculate Download Time
Use the tool above to calculate the download time easily. Just enter the file size and select the size units from the drop down. You can choose bits, bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, terabytes, petabytes, exabytes, zettabytes, and yottabytes. The time that is required the file will be calculated for multiple Internet connection speeds simultaneously. You can easily see the download time required for your Internet connection speed in the table.
The download time for a file depends on several factors, including the file size, internet connection speed, and network conditions. The formula to calculate download time is: Download Time = File Size / Download Speed
Here's a breakdown of the variables:
Download Time: The time it takes to download the file, typically measured in seconds, minutes, or hours.
File Size: The size of the file you are downloading, usually measured in bytes (B), kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), etc.
Download Speed: The speed at which your internet connection can download data, usually measured in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps).
It's essential to ensure that the file size and download speed are in the same units before performing the calculation. Here are some common download time scenarios:
Download Time in Seconds:
If you want the download time in seconds, and your download speed is in megabits per second (Mbps), use the formula:
Download Time (seconds)=File Size (megabits)Download Speed (Mbps)×8Download Time (seconds)=Download Speed (Mbps)File Size (megabits)×8
Download Time in Minutes:
If you want the download time in minutes, divide the result from the above formula by 60.
Download Time in Hours:
If you want the download time in hours, divide the result from the above formula by 3600 (60 seconds/minute × 60 minutes/hour).
Keep in mind that real-world download times may vary due to network congestion, latency, and other factors affecting your internet connection. Additionally, some download managers or web browsers may provide estimated download times as they take into account factors such as server responsiveness and parallel downloading.
What is Download Speed?
Download speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from a remote server or another device to your local device over the internet. It is measured in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps). Download speed is a crucial factor in determining how quickly you can retrieve files, stream videos, browse websites, and perform other online activities.
Here are the common units used to express download speed:
Bits per Second (bps): The smallest unit of data transfer speed. Often used for very small values.
Kilobits per Second (Kbps): Equal to 1,000 bits per second.
Megabits per Second (Mbps): Equal to 1,000 kilobits per second or 1,000,000 bits per second. This is a commonly used unit for measuring internet speeds.
Gigabits per Second (Gbps): Equal to 1,000 megabits per second or 1,000,000,000 bits per second. Higher-end internet connections and network speeds are often measured in gigabits per second.
When selecting an Internet plan, you'll typically see the download speed specified by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) in terms of Mbps or Gbps. Faster download speeds allow for quicker data retrieval, faster streaming, and smoother online experiences.
It's important to note that the actual download speed experienced by users can be influenced by various factors, including network congestion, the quality of the internet connection, the performance of the ISP's infrastructure, and the capabilities of the devices involved in the data transfer. Additionally, download speeds are only one aspect of overall internet performance, and factors such as upload speed, latency, and network stability also play crucial roles in determining the overall user experience.
Protocol overhead
Calculating the download time by dividing the size of the file by the connection speed (bit rate) may not be exact in a real-world scenario. This is because there are many factors that influence this process and reduce the speed. For example, the most common TCP/IP protocol transfers the data in packets which include some internal data that is needed for its operation. Such data is about 5% of the total data transferred.
For TCP over IPv4 over Ethernet you have (without header options):
- L1 overhead - preamble, IPG: 8+12 = 20
- L2 overhead - Ethernet header, FCS = 18
- L3 overhead - IPv4 header = 20
- L4 overhead - TCP header = 20
The L3 maximum packet size of 1500 results in a total L1 data size of 1500+18+20 = 1538 bytes and a maximum L4 payload size of 1500-20-20 = 1460 bytes.
- Overhead: 78/1538 *100% = 5.07%
- Efficiency: 1460/1538 *100% = 94.93%
Lost packets
There is also the "packet-loss" factor which may further reduce the transfer speed. As the information travels through many devices and over a very long distance some packets may get lost due to various reasons - bad cables, defective hardware, overloaded devices, etc. In such case, the lost packet is sent again from the server from where a file is downloaded which further reduces the bandwidth and increases the download time. In a properly working connection, such value is close to zero.
Server bandwidth
The download speed is determined not only by the connection speed of the downloading party but also the connection speed of the server that sends the data. If the server has slower connection speed than the receiving party then the maximum transfer speed is limited to one of the servers. Of course, in practice servers send data to multiple users simultaneously which may further reduce the transfer speed.
How Long It Takes to Download at 10Mbps
The time it takes to download various file types depends on several factors, such as the file size and your internet connection speed. Here, I'll provide some estimates for download times based on common file types and assuming a download speed of 10 Mbps, which is a moderate residential broadband speed. Keep in mind that these are rough estimates, and actual download times can vary.
Text Document (1 MB): Download Time: Approximately 0.8 seconds
High-Quality Image (5 MB): Download Time: Approximately 4 seconds
MP3 Audio (10 MB): Download Time: Approximately 8 seconds
PDF Document (20 MB): Download Time: Approximately 16 seconds
Standard Definition Video (700 MB): Download Time: Approximately 9 minutes
High Definition Video (2 GB): Download Time: Approximately 26 minutes
Software/Application (500 MB): Download Time: Approximately 6 minutes
Full-Length Movie (4 GB): Download Time: Approximately 43 minutes
These estimates are based on a download speed of 10 Mbps. If your internet connection speed is different, you can use the download time formula mentioned earlier to calculate more accurate estimates. Remember that these calculations assume optimal conditions and real-world download times may be influenced by network congestion, latency, and other factors.
What is Bandwidth?
Bandwidth, in the context of networking and internet communication, refers to the maximum rate of data transfer across a network. It represents the capacity of a network channel to transmit data over a specific period, usually measured in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps).
Here's a breakdown of the key concepts related to bandwidth:
Definition:
Bandwidth is the range or capacity of a communication channel, indicating how much data can be transmitted in a given time frame. It is not a measure of speed but rather a measure of capacity.
Units:
Bandwidth is typically measured in bits per second. The prefixes kilo, mega, and giga are commonly used to express larger values:
1 Kbps (Kilobit per second) = 1,000 bps
1 Mbps (Megabit per second) = 1,000 Kbps = 1,000,000 bps
1 Gbps (Gigabit per second) = 1,000 Mbps = 1,000,000 Kbps = 1,000,000,000 bps
Upstream vs. Downstream:
In internet connections, bandwidth is often categorized into upstream and downstream. Downstream bandwidth refers to the data flow from the internet to the user (downloads), while upstream bandwidth refers to the data flow from the user to the internet (uploads).
Shared Resource:
Bandwidth is a shared resource among all devices connected to a network. In shared networks, higher bandwidth allows for more data to be transmitted simultaneously, reducing congestion and improving performance.
Quality of Service (QoS):
The quality of service is affected by the available bandwidth. Higher bandwidth generally leads to a better user experience, particularly in activities such as streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing.
Symmetrical vs. Asymmetrical Bandwidth:
In symmetrical bandwidth, the upstream and downstream speeds are equal. In asymmetrical bandwidth, the speeds are different, with downstream often being faster than upstream. Asymmetrical bandwidth is common in consumer internet connections.
ISP Plans:
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) offer different plans with varying bandwidths to cater to the diverse needs of users. Faster download and upload speeds are often associated with higher-tier plans.
Understanding bandwidth is crucial for optimizing network performance and ensuring a smooth and efficient data transfer experience, especially in the context of internet connectivity and networking.
What's a good download speed?
A good download speed depends on your specific internet usage requirements and the number of devices connected to your network. Different online activities have different bandwidth requirements, and higher download speeds are generally beneficial for a smoother internet experience. As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, here are some general guidelines:
Basic Internet Use:
For light internet usage, such as web browsing and email, a download speed of 1 to 5 Mbps (megabits per second) is usually sufficient.
Streaming Standard-Definition (SD) Video:
For streaming SD video content on platforms like Netflix or YouTube, a download speed of at least 3 to 10 Mbps is recommended.
Streaming High-Definition (HD) Video:
For streaming HD video content, a speed of 5 to 25 Mbps is typically sufficient.
Online Gaming:
Online gaming usually requires low latency more than high download speeds. However, a download speed of 5 to 25 Mbps is generally suitable for most gaming activities.
Multiple Devices and HD Streaming:
In households with multiple devices and simultaneous HD video streaming, a download speed of 25 to 50 Mbps or higher is recommended.
4K Streaming and Large File Downloads:
For 4K video streaming and large file downloads, a speed of 50 Mbps or more is desirable.
Home Offices and Remote Work:
Home offices and remote work may benefit from higher speeds, especially if there are video conferences and large file transfers. Speeds of 50 Mbps to 100 Mbps or higher may be suitable.
High-Performance Activities:
For activities that demand high performance, such as large file uploads, heavy online gaming, or 4K video editing, speeds of 100 Mbps or more may be necessary.
It's important to note that these are general recommendations, and individual needs may vary. When choosing an internet plan, consider the number of users in your household, the types of online activities you engage in, and the overall demand on your network.
If you're unsure about your current internet speed or are considering an upgrade, you can use online speed test tools to check your download speed and compare it to your service plan. Additionally, consult with your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to discuss your specific requirements and available plans.
What is the average download speed in USA?
The average download speed in the USA varies based on factors such as location, internet service providers (ISPs), and the type of internet connection. Generally, urban areas and regions with access to fiber-optic or cable broadband services tend to have higher average download speeds compared to rural areas with limited infrastructure.
As of previous data, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) reported that the average download speed in the USA was around 180 Mbps (megabits per second) in 2020. However, keep in mind that this is an average, and individual speeds can vary widely.
It's advisable to check with your specific ISP or use online tools to test your current download speed, as these figures can change over time. Many ISPs provide tools on their websites that allow customers to check their current internet speeds. Additionally, speed test websites such as Ookla's Speedtest or Fast.com can provide real-time information on your internet speed.
For the most accurate and up-to-date information, consider checking with your local ISPs or relevant authorities that monitor internet speeds in your area.
How do I fix download time?
The download time of a file is primarily determined by your internet connection speed, which is influenced by factors such as your internet service plan, network congestion, and the efficiency of the servers hosting the file. If you're looking to optimize or "fix" download time, here are some tips:
-
Upgrade Your Internet Plan:
- Consider upgrading your internet service plan to one with higher download speeds. Faster plans often result in shorter download times.
-
Check Current Speed:
- Use online speed test tools to check your current download speed. This will give you an idea of the bandwidth you are currently experiencing.
-
Wired Connection:
- If you are using Wi-Fi, consider connecting to your router with an Ethernet cable. Wired connections are often more stable and provide faster speeds than Wi-Fi.
-
Close Background Applications:
- Make sure there are no other applications or devices on your network consuming bandwidth. This includes streaming services, online gaming, or large file uploads.
-
Choose Optimal Download Times:
- Downloading during off-peak hours, when network congestion is lower, might result in faster download speeds.
-
Use a Download Manager:
- Some download managers can optimize download speed by breaking files into smaller parts and downloading them simultaneously.
-
Choose Fast Servers:
- When downloading from websites, choose servers that are known to be fast and reliable. Some websites allow you to select a specific server for downloading files.
-
Update Your Router Firmware:
- Ensure that your router's firmware is up to date. Manufacturers occasionally release updates that can improve performance.
-
Consider a Content Delivery Network (CDN):
- For larger downloads, some services use CDNs to distribute the load across multiple servers, reducing download times.
-
Contact Your ISP:
- If you consistently experience slow download speeds, contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to troubleshoot and discuss potential solutions.
Remember that certain factors, such as the server's capacity and the overall health of the internet infrastructure, are beyond your control. If you've implemented the suggestions above and still experience slow download times, it's advisable to reach out to your ISP for further assistance.